Scientific Expedition on the Protection and Activation of Sino-Italian Urban Architectural Heritage in the Digital Age
The Sino-Italian International Architectural Heritage Protection and Activation Team from the School of Architecture and Urban Planning at Nanjing University conducted a four-day scientific expedition in Rome. Led by professors from the School of Architecture at the University of Rome, the team deeply explored historical sites such as the Colosseum, Palatine Hill, Piazza del Popolo, Piazza di Spagna, Trevi Fountain, Pantheon, Piazza Navona, and the Vittoriano Monument. Through field visits and academic lectures, team members gained an in-depth understanding of the history, culture, and architectural techniques of ancient Roman buildings, and learned about the close relationship between modern urban planning and archaeology and their roles in sustainable development. Additionally, the team visited Hadrian's Villa and the Villa d'Este, discussing the application of digital technology in architectural heritage protection. By visiting the Palace of Civilization and St. Peter's Basilica, the team gained insights into the evolution and innovation of architectural styles across different historical periods. This expedition not only broadened the team's academic horizons but also enhanced their understanding of architectural history and cultural heritage, inspiring thoughts on the integration of classical and modern architectural art.
July 11: Exploring the Splendor of Ancient Rome
On the afternoon of July 11, 2024, the Sino-Italian International Architectural Heritage Protection and Activation Team from the School of Architecture and Urban Planning at Nanjing University embarked on its highly anticipated scientific expedition, with the first stop being the Colosseum. Guided by a professor from the University of Rome, the team members delved into the history and culture of these ancient Roman buildings.
The professor from the University of Rome introduced that the Colosseum, built in AD 72, is one of the symbols of the ancient Roman Empire and was used for gladiatorial contests, animal hunts, and public spectacles. Team members learned about the construction techniques, functional layout, and historical background of the Colosseum, understanding its significant status in ancient Roman society. They were amazed by the grandeur and complex structure of the Colosseum, admiring the exceptional wisdom of Roman engineers and the superb craftsmanship of the workers.
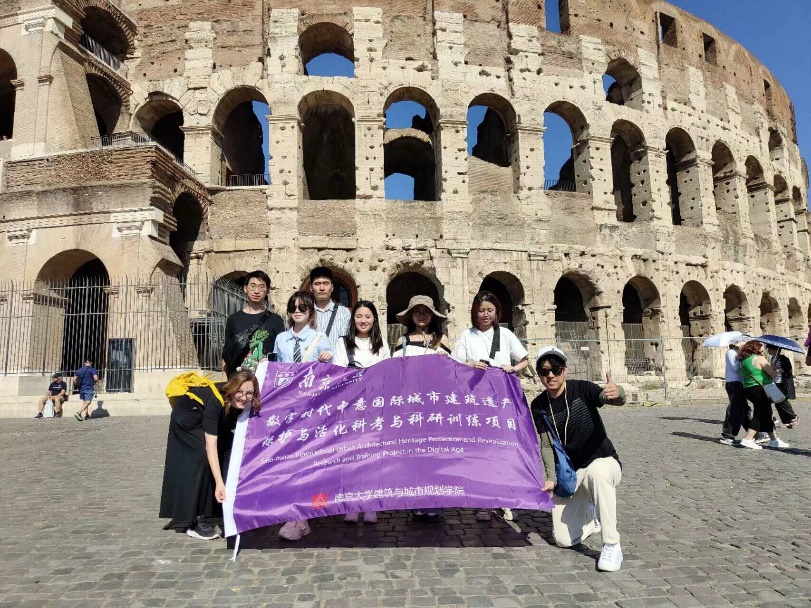

Group photo at the Colosseum
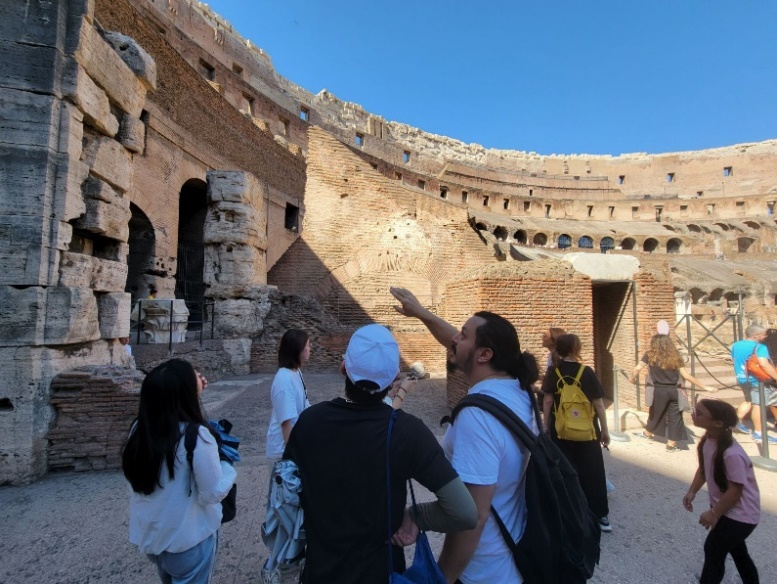

Professor from the University of Rome explaining
Next, the team ascended Palatine Hill, where the professor explained that it is the birthplace of ancient Rome, where, according to legend, Romulus, the founder of Rome, established the city. By visiting the palace ruins and archaeological sites on Palatine Hill, the team gained insights into the early history and culture of the Roman Empire. Under the professor's guidance, they witnessed the magnificent remnants of ancient palaces, igniting their passion for the protection and activation of architectural heritage.

Visiting Palatine Hill

Visiting ancient Roman ruins
Finally, the team visited other architectural ruins in ancient Rome, such as the Roman Forum and the Arch of Constantine. These buildings witnessed the glorious history of the Roman Empire and showcased the grandeur and exquisite craftsmanship of ancient architecture. The team paused in front of these historical sites, as if traveling through time, experiencing the daily life and significant events of ancient Romans.

Explaining ancient Roman ruins

Explaining the Arch of Constantine
July 12: Discussion with Faculty and Students from the University of Rome
On July 12, the Sino-Italian International Architectural Heritage Protection and Activation Team from the School of Architecture and Urban Planning at Nanjing University conducted an in-depth architectural study in Rome. This journey not only allowed everyone to appreciate the grandeur and intricacy of Roman architecture but also deepened their understanding and research of ancient and modern architectural art through academic exchanges with the University of Rome.
In the morning, the Nanjing University Expedition Team attended a series of lectures hosted by the University of Rome. The lectures focused on the archaeological sites and urban planning of Rome, including three thematic presentations: "Living Amidst the Ruins: Archaeological Sites as Hubs of Biodiversity and for Sustainable Development," "Urban Planning and Archaeology in Contemporary Rome: An Interdisciplinary Challenge," and "Study Trip to Rome." Through these lectures, we gained a deep understanding of the close relationship between Roman archaeology and modern urban planning and its role in sustainable development.

Lecture 1: Living Amidst the Ruins Archaeological Sites as Hubs of Biodiversity and for Sustainable Developmen
The first lecture was delivered by Alessandra Capuano, Head of the Department of Architecture at the University of Rome. From the perspective of biodiversity, the professor explored the unique value of archaeological sites in modern cities. Rome, with its rich historical relics, not only forms an essential part of cultural heritage but also serves as crucial sites for biodiversity conservation. In the lecture, the professor showcased multiple archaeological sites transformed into significant ecological green spaces in the city through ecological restoration and green design, providing new ideas and examples for sustainable development.

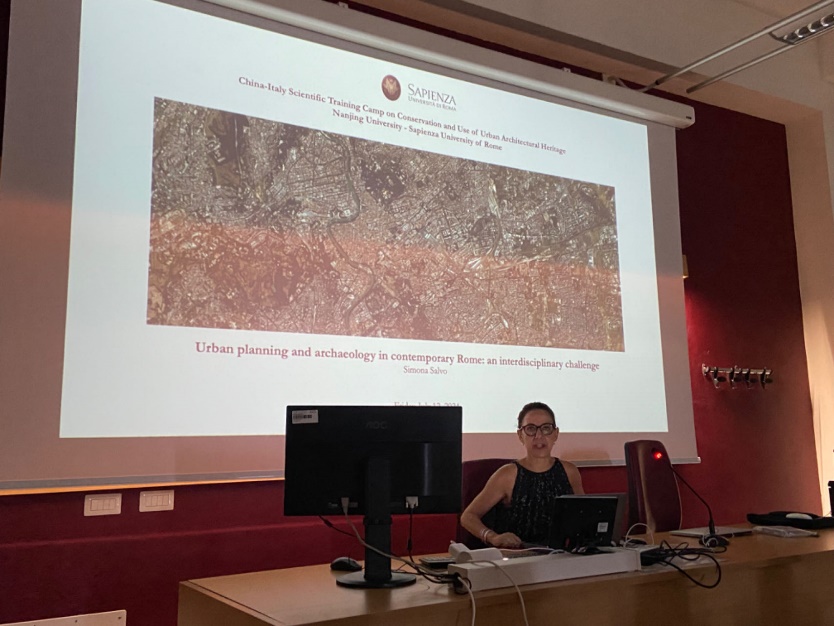
Lecture 2: Urban planning and archaeology in contemporary Rome: an interdisciplinary challenge
The second lecture, delivered by Professor Simona Salvo, emphasized the crucial role of archaeology in urban planning. Rome, with its long history, needs to balance protecting historical relics and meeting modern urban development needs during urban planning and construction. Experts demonstrated through specific cases the key role of interdisciplinary collaboration in addressing this challenge and how to protect and showcase archaeological sites in urban construction.

Lecture 3: Study Trip to Rome
The third lecture was a thematic sharing session titled "Study Trip to Rome," delivered by Professor Nilda Valentin. This lecture introduced multiple archaeological sites and significant buildings in Rome, providing a deep understanding of the history and cultural stories behind these sites and buildings. In the lecture, experts detailed the excavation history, archaeological discoveries, and current status of protection and utilization of various sites. Through field visits and explanations, we not only experienced the rich historical relics of Rome firsthand but also learned how to promote the organic integration of heritage with modern urban life while protecting it.

By attending these three lectures, members of the Nanjing University Expedition Team gained a profound understanding of the close ties between archaeology, modern urban planning, and ecological conservation. This academic exchange not only broadened our research horizons but also provided valuable experiences and insights for our future academic research and practical work.
The afternoon exploration began at Piazza del Popolo. This grand square is the main entrance to northern Rome and has been an important gathering place for citizens since ancient times. The team took a group photo here, feeling the classical atmosphere of Rome. Next, the team visited Piazza di Spagna, Trevi Fountain, the Pantheon, Piazza Navona, and the Vittoriano Monument, further learning and understanding the protection and reconstruction of ancient Roman architecture in practice, and strengthening exchanges with the University of Rome.
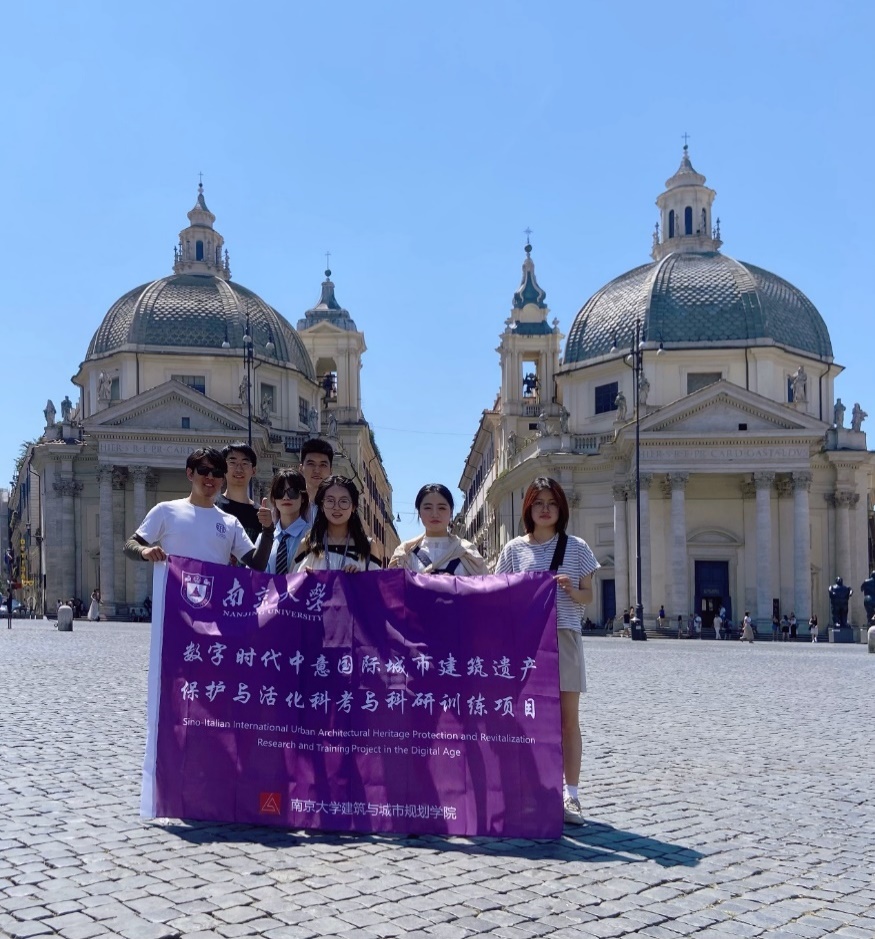

Group photo at Piazza del Popolo
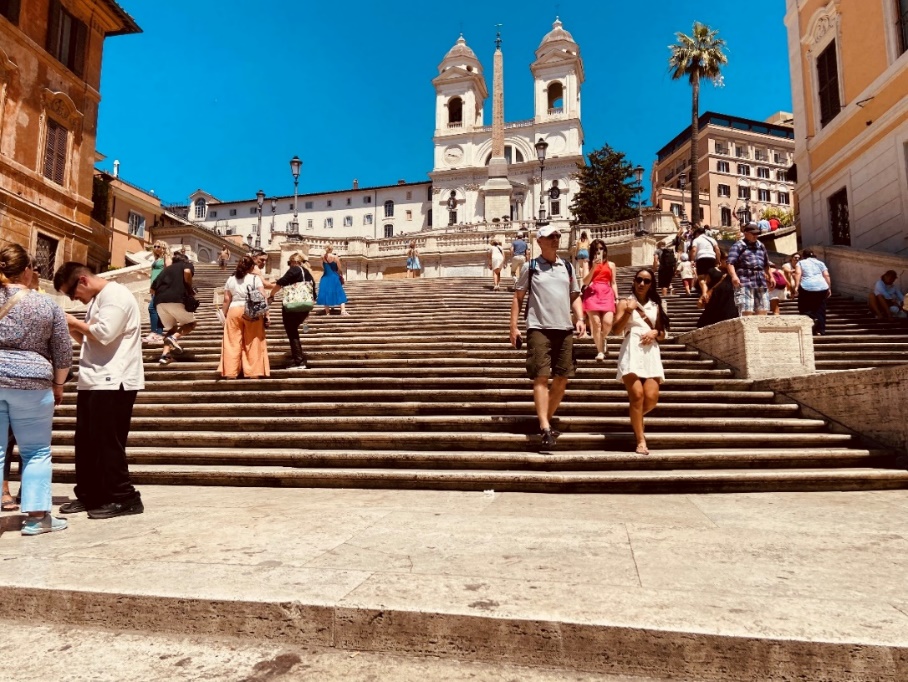

Piazza di Spagna
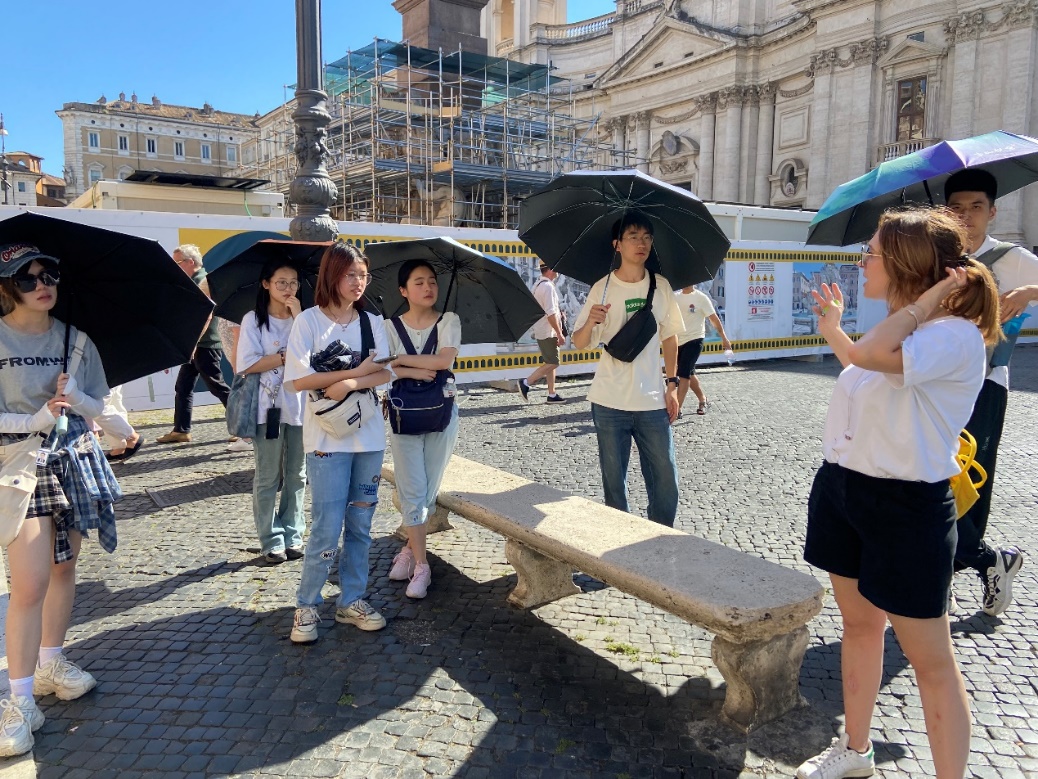

Group photo at Piazza Navona
At the end of the day, members of the Nanjing University Expedition Team gained a deeper understanding of Rome's rich architectural heritage. This expedition not only broadened our academic horizons but also inspired our thoughts on the integration of classical and modern architectural art.
July 13: Visiting Hadrian's Villa and Villa d'Este
On July 13, the expedition continued, visiting two famous ancient sites near Rome: Hadrian's Villa and Villa d'Este.
The professor pointed out that Hadrian's Villa was a private villa built by Roman Emperor Hadrian in the 2nd century AD, covering a vast area with diverse architectural styles. The team visited luxurious palaces, baths, theaters, and gardens here, learning about the architectural layout and design concepts of Hadrian's Villa. They not only gained rich historical knowledge but also experienced the importance of digital technology in architectural heritage protection.
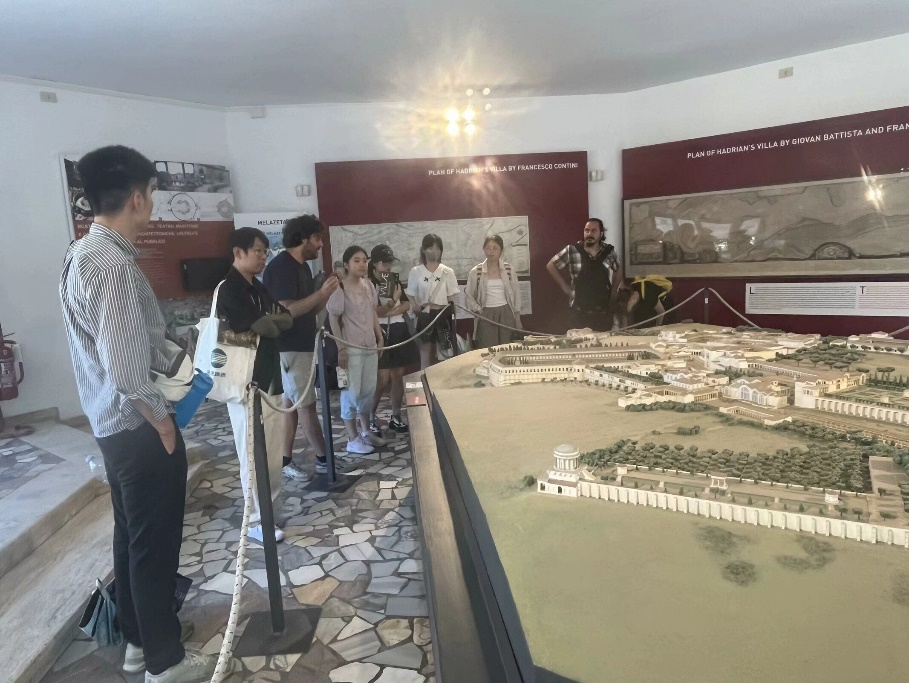
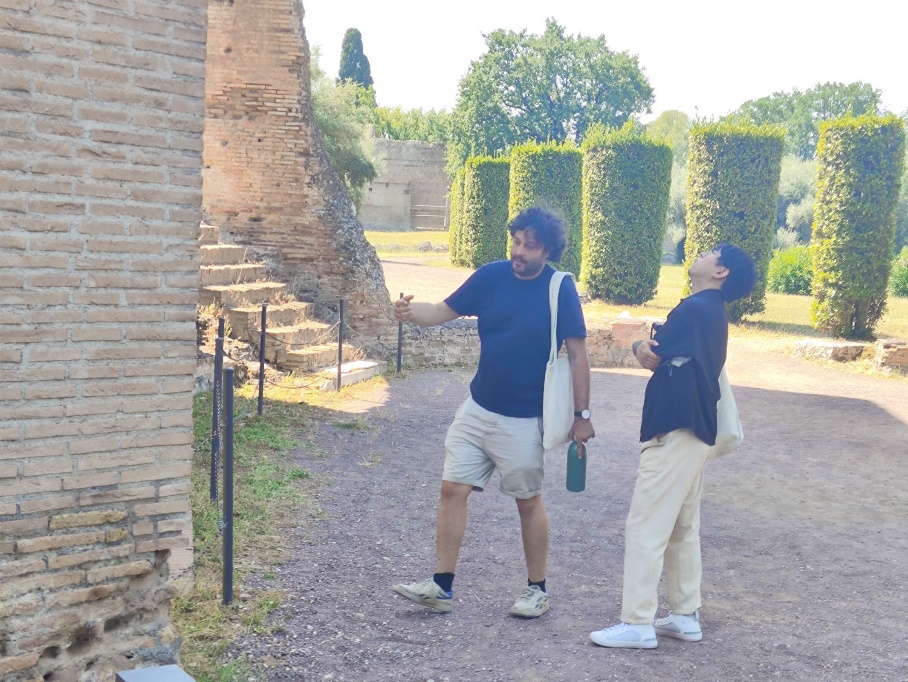



Explanation at Hadrian's Villa
Next, the team visited Villa d'Este, a Renaissance masterpiece built by Cardinal Ippolito d'Este, famous for its beautiful gardens and fountains. The team admired the exquisite frescoes and sculptures in the villa, learned about the artistic styles and architectural features of the Renaissance, and discussed with professors how to protect and showcase these precious cultural heritages in modern environments.
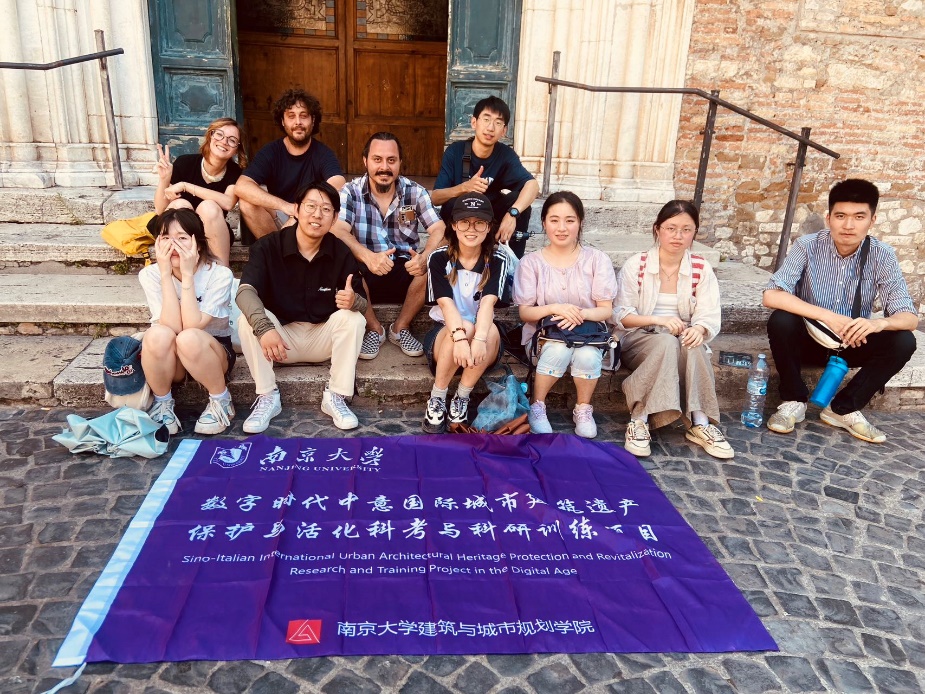

Group photo at Villa d'Este
July 14: In-Depth Architectural Study
On July 14, the expedition team continued their in-depth architectural study in Rome, focusing on two significant buildings: the Palace of Civilization and St. Peter's Basilica. These two buildings represent different historical periods and architectural styles, adding rich academic value and cultural experience to the expedition.
In the morning, the team first visited the Palace of Civilization. The Palace of Civilization is one of the representative works of Italian Fascist architecture, reflecting the combination of Neoclassicism and Modernism.
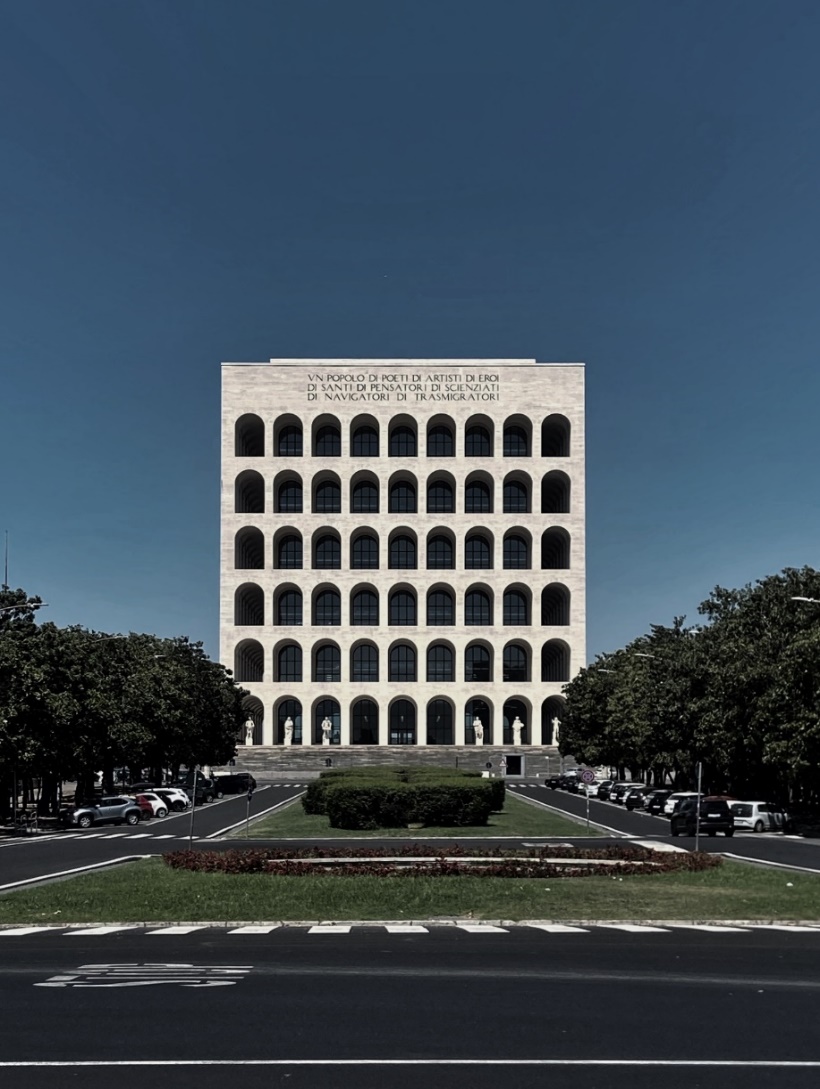

Palace of Civilization
The exterior of the Palace of Civilization is known for its square cubic shape and orderly arcades, hailed as the "Square Colosseum." The symmetrical layout and simple lines of the building highlight solemnity and strength. Each floor of the exterior facade has six arches, symbolizing the six fundamental elements of Italian unity and revival. The interior space design also emphasizes symmetry and proportion, creating a grand and sacred atmosphere through the clever introduction of natural light.
In the afternoon, the team went to St. Peter's Basilica for an in-depth study. Located in Vatican City, St. Peter's Basilica is one of the largest Christian churches in the world and the center of the Catholic Church. Its design incorporates elements of the ancient Roman Pantheon and showcases the Renaissance pursuit of perfect proportions and geometric forms.
We also paid special attention to St. Peter's Square in front of the basilica. The square adopts an elliptical design, symbolizing the embracing arms of St. Peter, with an obelisk standing in the center, surrounded by 284 Doric columns, showcasing the perfect fusion of classical and Baroque styles.
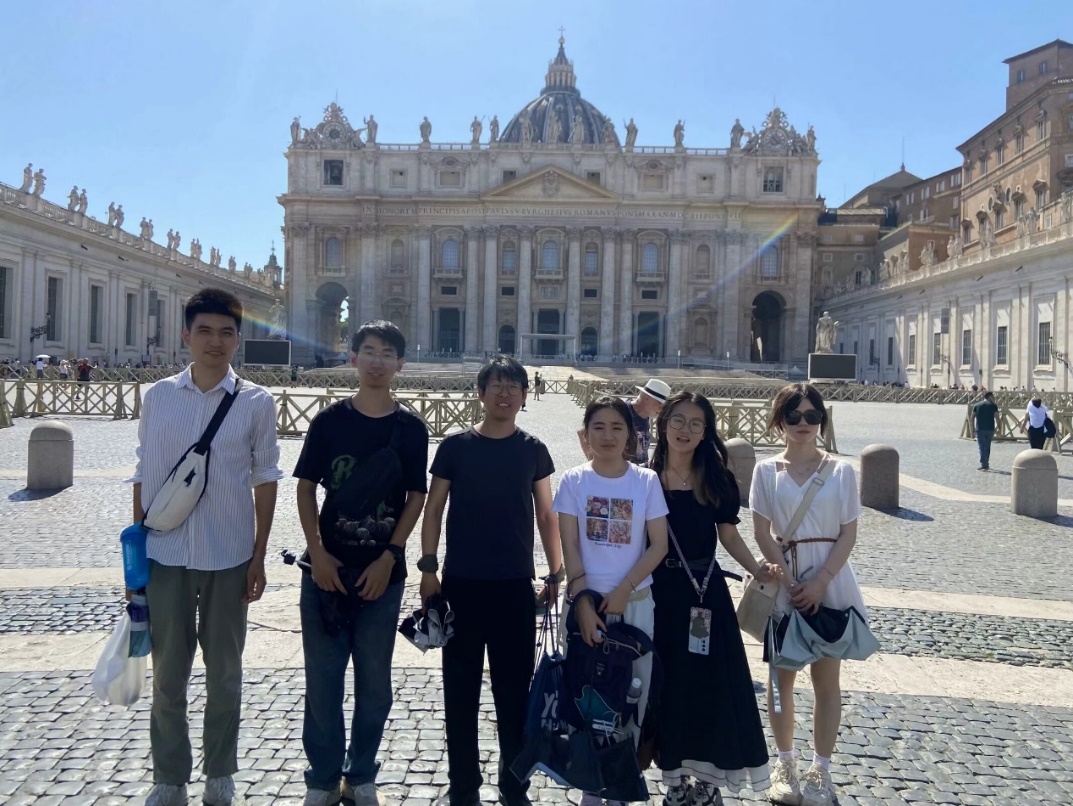

Group photo at St. Peter's Basilica
This visit deepened our understanding of the diversity and innovation of architectural styles in different historical periods. Through in-depth observations and learning about these two significant buildings, the team members gained a comprehensive understanding of the development and evolution of architectural art.
Conclusion:
Through this four-day scientific expedition, the Sino-Italian International Architectural Heritage Protection and Activation Team from the School of Architecture and Urban Planning at Nanjing University has had an unprecedented academic experience. The architectural study in Rome has allowed us to appreciate the grandeur and intricacy of Roman architecture, deepening our understanding of the historical significance and contemporary value of architectural heritage. This expedition has not only broadened our academic horizons but also provided valuable experiences and insights for our future research and practical work in the field of architectural heritage protection and activation.